Introduction : Heat Class 7th Science
In this post we are going to discuss a very simle yet very important topic i.e. Heat for Class 7th Science.
Heat is a form of energy that is related to the temperature of an object or substance. It is caused by the movement of tiny particles called atoms or molecules. Heat can be transferred from one place to another through various methods, such as conduction, convection, and radiation.
Understanding heat and how it is transferred is important in many fields of science and technology.
Concept of Hot and Cold

In general, hot refers to a high temperature, while cold refers to a low temperature. These terms are often used to describe the temperature of objects or substances, such as food or drinks. For example, coffee is hot when it has a high temperature, while ice cream is cold when it has a low temperature.
Hot and cold can also be used to describe the temperature of a place or environment, such as a hot day or a cold winter.
How Heat And Temperature are Measured
Temperature is a measure of the heat energy of a substance or environment. It is typically measured in units of degrees, such as degrees Celsius (°C) or degrees Fahrenheit (°F) or in Kelvin.
The Celsius scale is a metric scale in which the freezing point of water is 0 degrees and the boiling point of water is 100 degrees. The size of the degree unit on the Celsius scale is the same as the size of the degree unit on the Kelvin scale.
The Fahrenheit scale is a non-metric scale in which the freezing point of water is 32 degrees and the boiling point of water is 212 degrees. The size of the degree unit on the Fahrenheit scale is smaller than the size of the degree unit on the Celsius scale.
The Kelvin scale is a metric scale in which the size of the degree unit is the same as the size of the degree unit on the Celsius scale. Zero on the Kelvin scale is absolute zero, which is the temperature at which all molecular motion ceases.
So, the main difference between these scales is the size of the degree unit and the zero point of the scale.

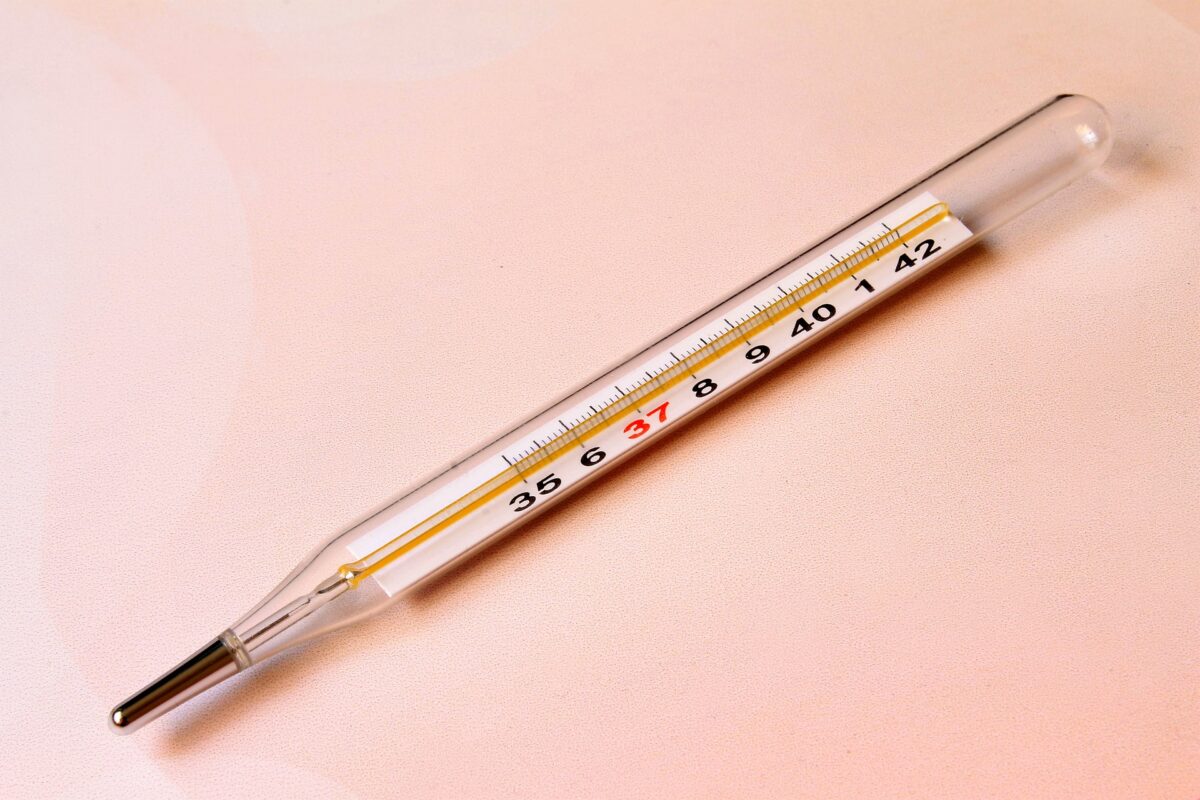
A device used to measure temperature is called thermometer. It can be used in a variety of settings, including in the home, in a laboratory, or in an industrial setting.
A clinical thermometer is a type of thermometer that is specifically designed to be used in a medical setting to measure the body temperature of a patient. Clinical thermometers are typically more accurate and precise than other types of thermometers. They are also usually easier to use, as they are designed to be used by people who may not have extensive training in thermometry.
One of the main differences between a thermometer and a clinical thermometer is their intended use. Clinical thermometers are intended for use in a medical setting to measure the body temperature of a patient, while thermometers can be used in a variety of settings to measure different types of temperatures.
Clinical thermometers are also typically more accurate and precise than other types of thermometers, as the body temperature of a patient needs to be measured with a high degree of accuracy in order to properly diagnose and treat medical conditions.
Transfer of Heat
Conduction
Heat conduction is the transfer of heat from one body to another as a result of a temperature difference between the two bodies. It occurs when heat is transferred through a material by the movement of atomic or molecular particles. In other words, heat is conducted through a material when the particles that make up the material vibrate or collide with each other, transferring their energy from one particle to the next.
Heat is conducted more better in some materials than others. Materials that are good conductors of heat, such as metals, allow heat to be transferred quickly and easily. Materials that are poor conductors of heat, such as wood or plastic, do not transfer heat as efficiently.
Convection
Heat transfer through convection occurs when a fluid, such as a gas or liquid, is in contact with a solid surface that is at a different temperature. As the fluid comes into contact with the surface, heat is transferred from the hotter surface to the cooler fluid, causing the fluid to become warmer. This warmer fluid then rises, and as it does so, it carries the heat away from the surface.
As the hot fluid rises and moves away from the surface, cooler fluid flows in to take its place, and the process is repeated. This continuous circulation of fluid, caused by the difference in density between the hot and cool fluids, is known as convection. Convection is an important mode of heat transfer in many natural and man-made systems, and it plays a crucial role in many practical applications, such as in heating and cooling systems and in the transfer of heat in the Earth’s atmosphere and oceans.
Radiation
Heat transfer through radiation occurs when heat is transmitted through electromagnetic waves, such as infrared radiation. This type of heat transfer does not require a medium, such as a fluid or a solid, to transmit the heat. Instead, heat is transferred through the vacuum of space, or through the air, by means of electromagnetic waves.It is the primary means by which heat is transferred from the sun to the Earth.